Summary
Welcome to my software page! Stick around to check out the following projects that I have completed in software development:
- Project 1 - Autonomous Sailboats: UBC Sailbot
- Project 2 - Cellular Simulation: UBC Bootcamp
UBC Sailbot
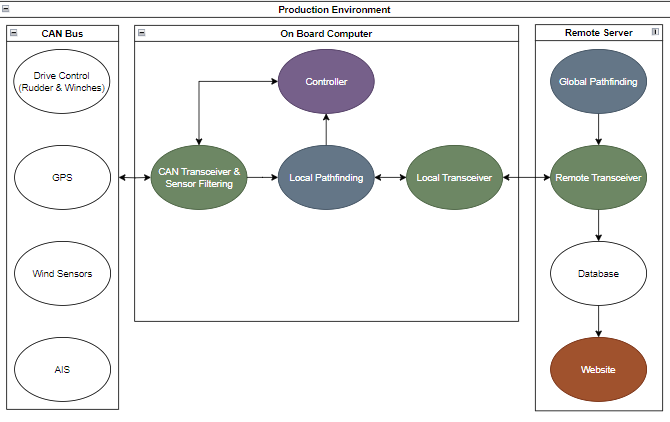
At UBC Sailbot, we are developing an autonomous sailboat called Polaris. The goal is to design a boat capable of navigating waterways without human intervention. Sailbot has been building autonomous sailboats for several years. Another key objective is to collect various types of ocean data, including environmental measurements such as wind speed, temperature, and GPS location, which can support scientific research. I am part of the Network Systems Team, responsible for developing the boat’s remote transceiver, which serves as the interface between the main computer onboard and the land-based server.

Key contributions:
Skills/Tools: C++, Satellite Communication
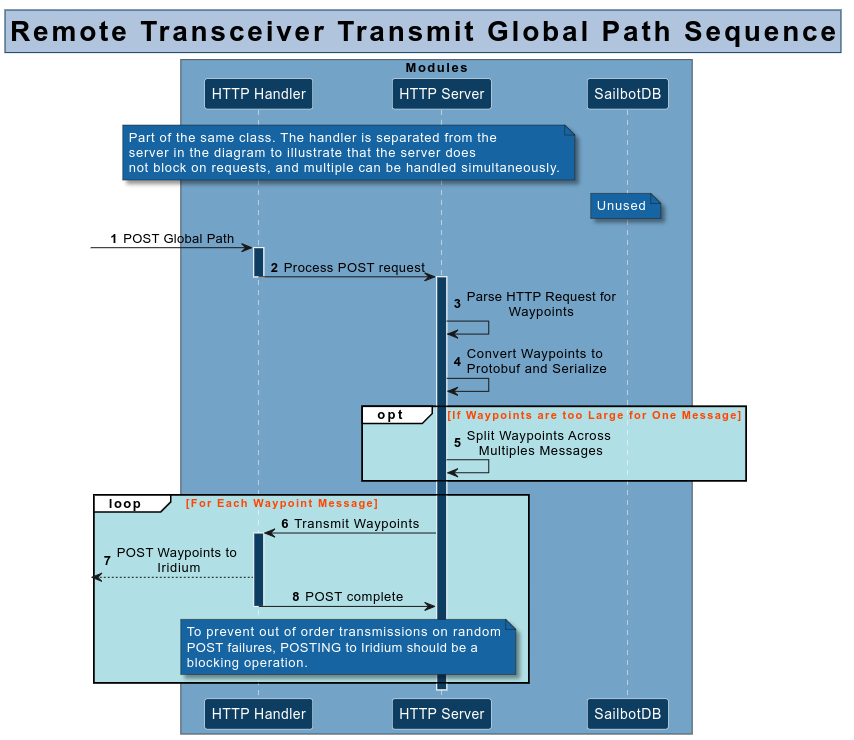
Developed the remote transceiver for UBC Sailbot's autonomous sailboat, enabling reliable communication between the boat’s main computer and a remote server via the Iridium satellite network.Skills/Tools: JSON, Google Protobuf
Parsed and processed global path JSON data from the Global Pathfinding team and serialized it using Google Protobuf to ensure data integrity.Skills/Tools: MongoDB, Database Design
Implemented storage of global path waypoints and timestamps in MongoDB for persistent and efficient data retrieval.Skills/Tools: libcurl, HTTP Protocol
Designed robust HTTP communication using libcurl to transmit serialized data and handle server responses with error verification.Skills/Tools: Google Test Framework, C++, Multithreading
Debugged and tested Iridium responses by automating multithreaded POST requests to improve system reliability.Summary of Skills
















Autonomous Navigation
In order for the boat to travel through the ocean, it is essential that it contains algorithms that provide the best possible paths for the boat to go through based on real-time data and pre-defined objectives. These algorithms are based on multiple factors such as wind direction, current, obstacles, and waypoints, ensuring that the boat can navigate efficiently and autonomously. This is the objective of the Global Pathfinding team, to continuously update and send waypoint data to the network systems team, enabling real-time adjustments and ensuring the boat stays on course by transmitting information about its position and planned route to the remote server.
My Role
As being responsible for the development for the remote transceiver, I was mainly focused on achieving the following objectives:
- Enabling data transmission between the boat’s main computer and the remote server via the Iridium satellite network
- Verifying HTTP API calls with ROCKBLOCK servers to transmit global path data and process server responses
- Storing the global path waypoints received from the Global Pathfinding team in the MongoDB database
- Verifying accurate storage of global path waypoints in the MongoDB database
Code Implementation
Cell Simulation and Automata
Participated in a biomedical engineering bootcamp where I worked on a project simulating cellular interactions between various cell types, playing the role of a researcher at the School of Biomedical Engineering (SBME). My main objective was to help clinicians better understand complex cell interactions and aid in medical decisions.
The goal of this project is to:
- Help illustrate the need for object-oriented programming in a biomedical context
- Implement various object-oriented programming paradigms
- Understand the relevancy and methodology of translating clinical requirements into your project
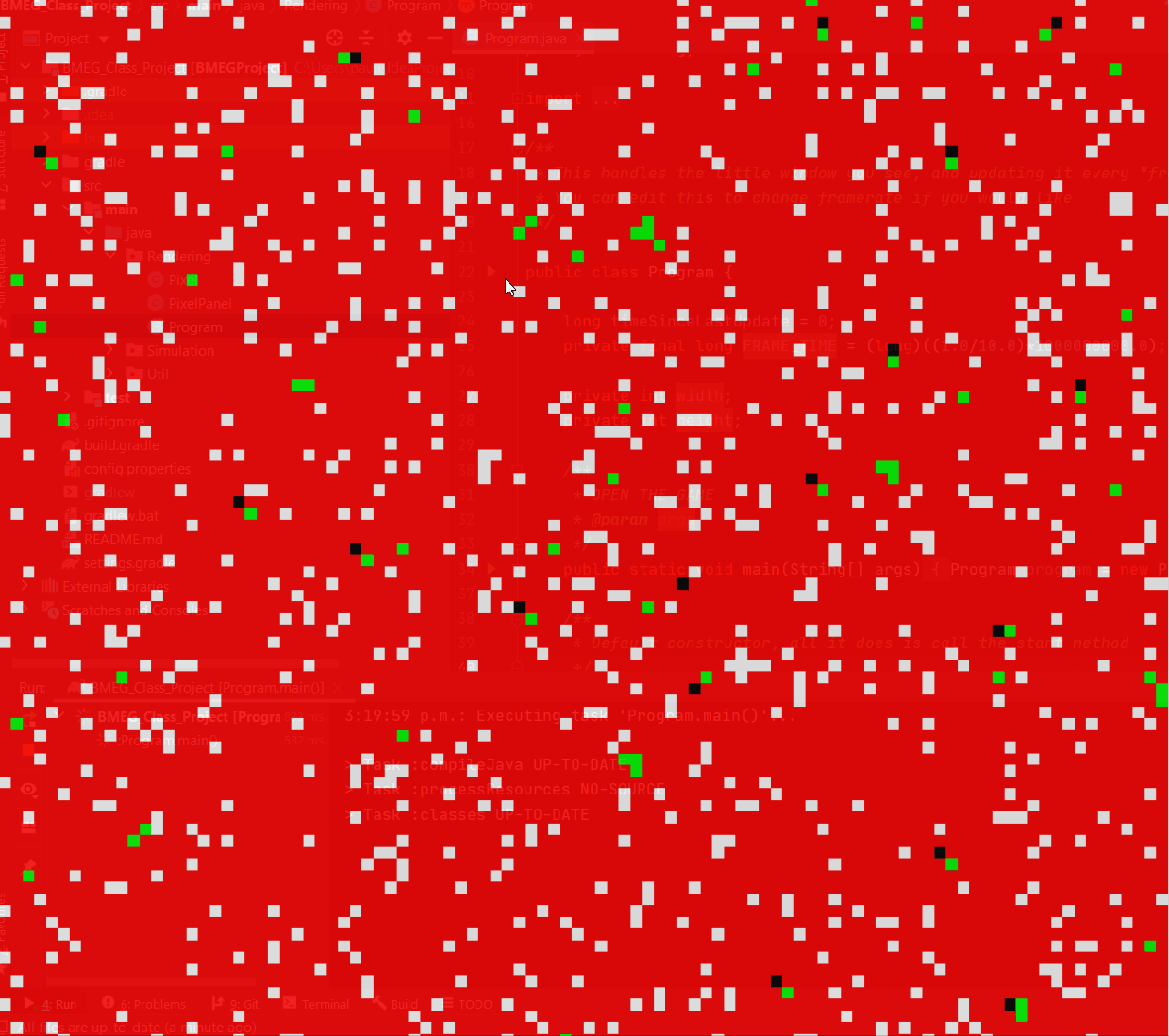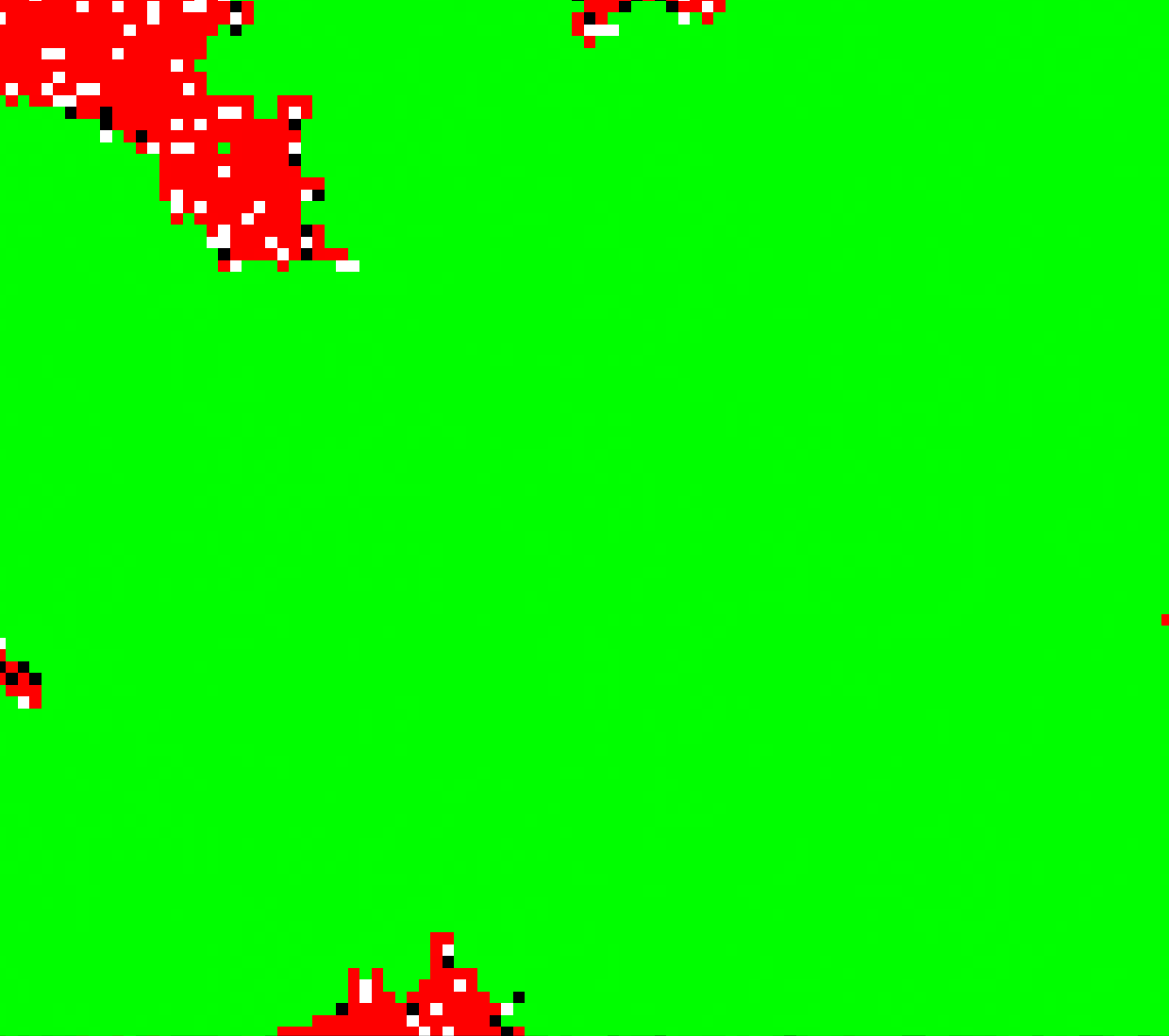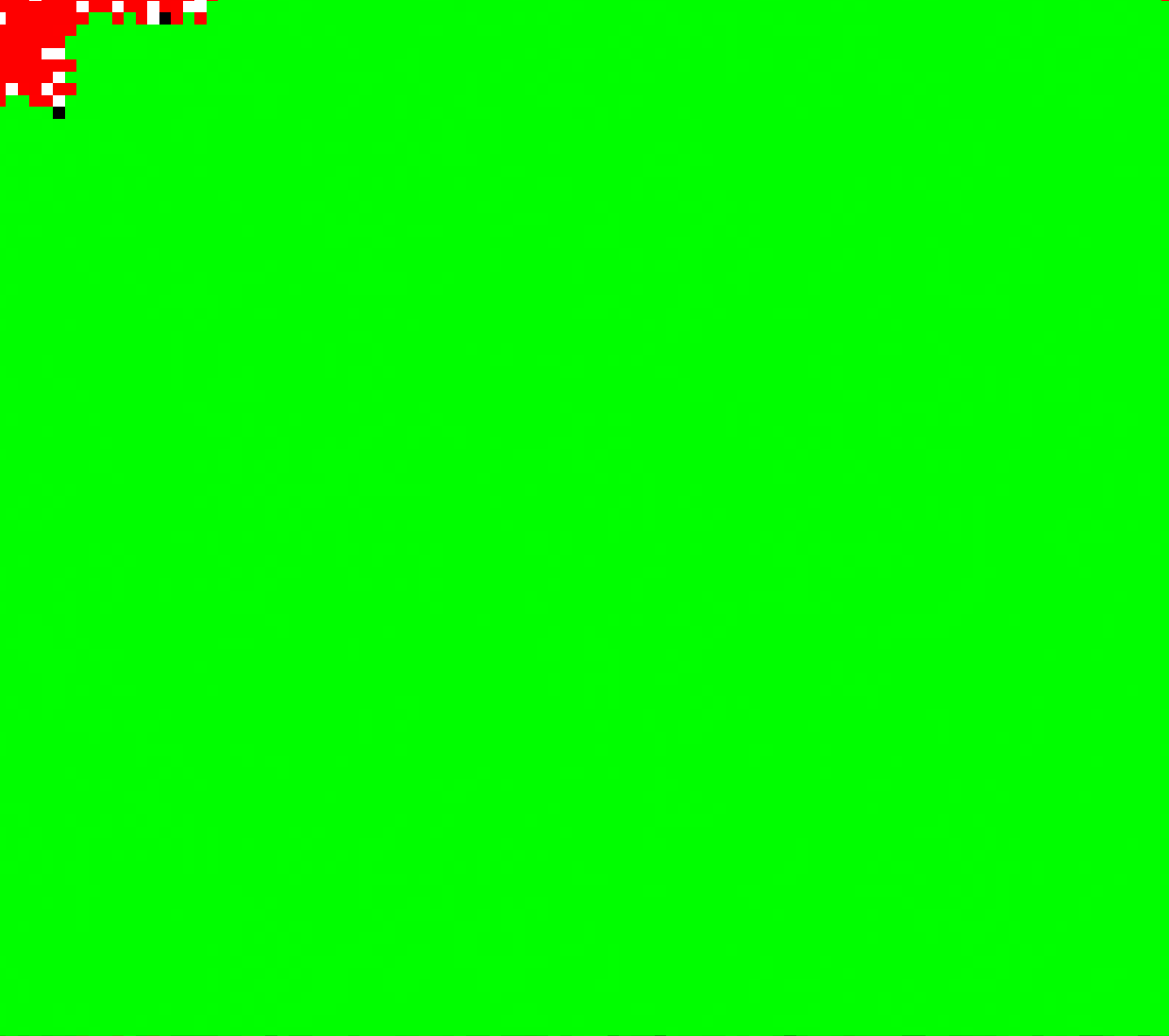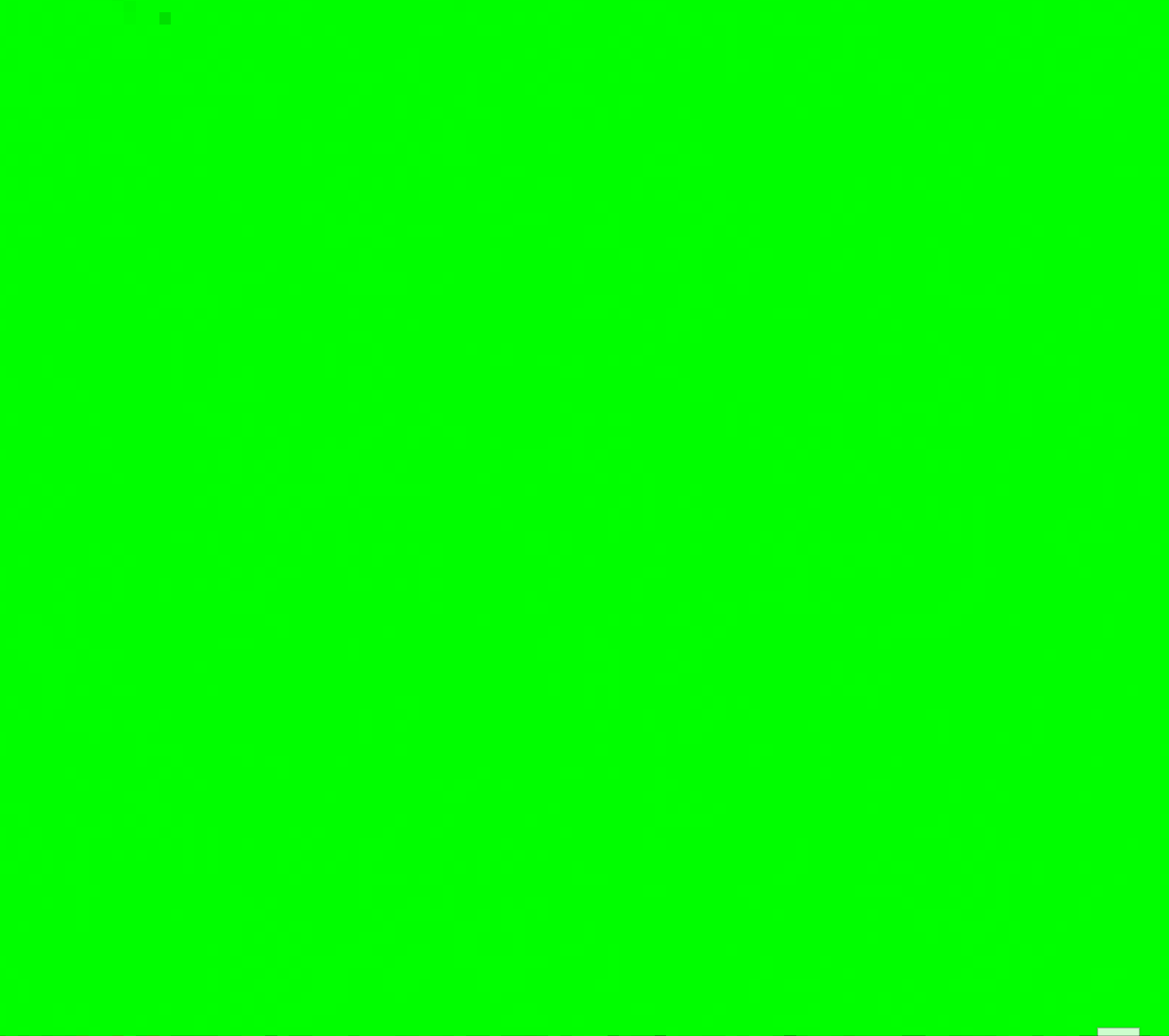
Key contributions:
-
Designed and implemented a cellular automata simulation for cancer and human cells.
Skills/Tools: Java, IntelliJ IDEA, Object-Oriented Programming
-
Developed four types of cells with distinct behaviors: ImmuneCell, TissueCell, DeadCell, CancerCell.
Skills/Tools: Java, Class Design, System Modeling
-
Implemented neighborhood-based rules for each cell to interact with surrounding cells, mimicking real biological behavior.
Skills/Tools: Algorithm Design, Cellular Automata, Simulation
-
Visualized simulation results for demonstration and analysis of cell interactions.
Skills/Tools: Java Swing, Data Visualization
Cellular Automata Explanation:
A cellular automaton is a system where objects interact based on a set of rules. Features include:
- Objects embedded in a 2D grid
- Each object has a state (e.g., 0/off or 1/on)
- Each object interacts with adjacent neighbors
Neighborhood example for coordinates (x,y):
| (x-1,y-1) | (x,y-1) | (x+1,y-1) |
|---|---|---|
| (x-1,y) | (x,y) | (x+1,y) |
| (x-1,y+1) | (x,y+1) | (x+1,y+1) |
Inspired by Conway’s Game of Life, demonstrating complex behavior from simple rules.
The following cells are implemented:
ImmuneCell
- Specialized in fighting
CancerCells - Scans neighborhood for
CancerCells - Targets and eliminates one
CancerCellsat a time - Replaces eliminated
CancerCellswithDeadCell
TissueCell
- Focuses on growth and regeneration
- Examines surrounding area for
DeadCells - If a
DeadCellexists, it will “grow” into a newTissueCellby replacing theDeadCellwith aTissueCell
DeadCell
- Passive cell type with no active functions
- Serves as placeholder in the simulation
- Exists only to be interacted with by other cell types
- Important for system balance
CancerCell
- Most sophisticated cell behavior in simulation
- Looks at its neighborhood and counts the number of dead, tissue, and immune cells around it, while also storing their location
- Then chooses one of 4 actions depending on its local environment:
- If there are any dead cells, the cancer will choose one and "grow" into it, replacing it with a new
CancerCell - If the number of tissue cells is greater than the number of immune cells, it will choose one and kill it, replacing it with a
DeadCell - If the number of immune cells is greater than the number of tissue cells, it will attack an immune cell, potentially killing it
- If the cancer cell is entirely surrounded by cancer cells then it will do nothing
- If there are any dead cells, the cancer will choose one and "grow" into it, replacing it with a new
Code Implementation
public class ImmuneCell extends Cell{
public ImmuneCell(int xInput, int yInput){
super(3, xInput, yInput, 4);
}
public ImmuneCell(Pair coord){
super(3, coord.getX(), coord.getY(), 4);
}
@Override
public void interactNeighbors(ArrayList<Cell> neighbors){
int count = 0;
double rand = 0;
ArrayList<Integer> cells = collectNeighbors();
int i = 0;
int min = 0;
for(int x: cells) {
if (x >= 0 && x < neighbors.size() && neighbors.get(x).getId() == 3) {
count++;
}
}
int max = count;
int[] arr = new int[count];
if(count > 0) {
for (int x : cells) {
if (x >= 0 && x < neighbors.size() && neighbors.get(x).getId() == 3) {
arr[i] = x;
i++;
}
}
int random_int = (int)Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min) + min);
Pair coordinates = Calculator.coordFromIndex(arr[random_int]);
neighbors.set(arr[random_int], new DeadCell(coordinates));
}
}
}
public class TissueCell extends Cell{
public TissueCell(int xInput, int yInput){
super(0, xInput, yInput,1);
}
public TissueCell(Pair coord){
super(0, coord.getX(), coord.getY(), 1);
}
@Override
public void interactNeighbors(ArrayList<Cell> neighbors){
ArrayList<Integer> cells = collectNeighbors();
for (int x : cells) {
if (x >= 0 && x < neighbors.size() && neighbors.get(x).getId() == 0) {
if (Math.random() < 0.7) {
Pair coordinates = Calculator.coordFromIndex(x);
neighbors.set(x, new TissueCell(coordinates));
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public class DeadCell extends Cell{
public DeadCell(int xInput, int yInput){
super(0, xInput, yInput, 0);
}
public DeadCell(Pair coord){
super(0, coord.getX(), coord.getY(), 0);
}
}
public class CancerCell extends Cell{
public CancerCell(int xInput, int yInput){
super(1, xInput, yInput, 3);
}
public CancerCell(Pair coord){
super(1, coord.getX(), coord.getY(), 3);
}
@Override
public void interactNeighbors(ArrayList<Cell> neighbors){
ArrayList<Integer> cells = collectNeighbors();
int DeadNeighbor = 0;
int TissueNeighbor = 0;
int ImmuneNeighbor = 0;
int i = 0;
int min = 0;
for(int x: cells){
if(x >= 0 && x < neighbors.size()) {
if (neighbors.get(x).getId() == 0) {
DeadNeighbor++;
} else if (neighbors.get(x).getId() == 1) {
TissueNeighbor++;
} else if (neighbors.get(x).getId() == 4) {
ImmuneNeighbor++;
}
}
}
int[] arr1 = new int[TissueNeighbor];
for(int x: cells) {
if (x >= 0 && x < neighbors.size() && neighbors.get(x).getId() == 1) {
arr1[i] = x;
i++;
}
}
int max = TissueNeighbor;
int[] arr2 = new int[ImmuneNeighbor];
i = 0;
for(int x: cells) {
if (x >= 0 && x < neighbors.size() && neighbors.get(x).getId() == 4) {
arr2[i] = x;
i++;
}
}
int max2 = ImmuneNeighbor;
if(DeadNeighbor > 0){
for(int x: cells){
if(x >= 0 && x < neighbors.size() && neighbors.get(x).getId() == 0){
Pair coordinates = Calculator.coordFromIndex(x);
neighbors.set(x, new CancerCell(coordinates));
break;
}
}
} else if(TissueNeighbor > ImmuneNeighbor && TissueNeighbor >= 1){
int random_int = (int)Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min) + min);
Pair coordinates = Calculator.coordFromIndex(arr1[random_int]);
neighbors.set(arr1[random_int], new DeadCell(coordinates));
} else if(ImmuneNeighbor > 0){
int random_int = (int)Math.floor(Math.random() * (max2 - min) + min);
int newStrength = neighbors.get(arr2[random_int]).getStrength() - 1;
neighbors.get(arr2[random_int]).setStrength(newStrength);
Pair coordinates = Calculator.coordFromIndex(arr2[random_int]);
neighbors.set(arr2[random_int], new DeadCell(coordinates));
}
}
}
Summary of Skills







